Accessory Drive Belt System
|
|
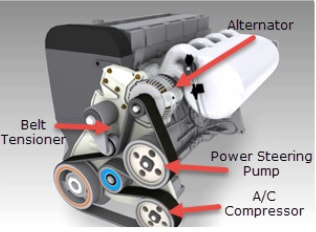
The accessory drive belt is made of a synthetic rubber compound and drives
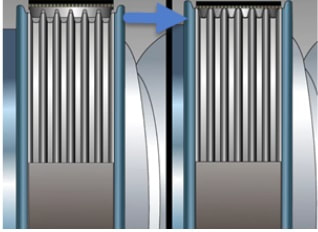
accessories on the vehicle such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. The belt tensioner puts tension on the drive belt to keep the belt in place and to create sufficient friction to turn all the pulleys on the belt system. Recent technology improvements in belt construction mean that belts do not develop cracks, even when they are worn. A new belt will come in contact with the drive pulley on the sides of the ribs only. As the belt wears, the ribs become thinner and thinner and when the belt is completely worn, the belt rides on the peaks of the drive pulley. This reduces the grip between the belt and pulley and causes the belt to squeal. When the belt tensioner becomes weak, the belt is not wrapped tightly enough around the pulleys, potentially resulting in slipping, especially on components that require a lot of energy to rotate, such as the alternator. This can result in squealing noises and reduces accessory efficiency. A misaligned belt tensioner - where the surface of the tensioner pulley doesn' t run parallel with the belt and other pulleys - can occur with automatic spring tensioners. The misaligned tensioner pulley puts greater pressure on a small section of the belt, which eventually causes a rib or multiple ribs to become detached from the belt. Idler pulleys are used to route the belt to the different components of the accessory drive belt system. Inside the pulley is a sealed bearing which can eventually fail. A failed bearing causes the pulley to stop turning. The rotating belt rubs against the seized pulley surface, generating a lot of heat and noise until the belt breaks. With a broken belt, the vehicle can become un drive able. |